Thalassemia in India
Blood Warriors
April 15, 2025
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that results in the production of abnormal hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. There are two main types of thalassemia: alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia. Alpha thalassemia occurs when there is a deficiency in the production of alpha globin, a subunit of hemoglobin, while beta thalassemia occurs when there is a deficiency in the production of beta globin, another subunit of hemoglobin.
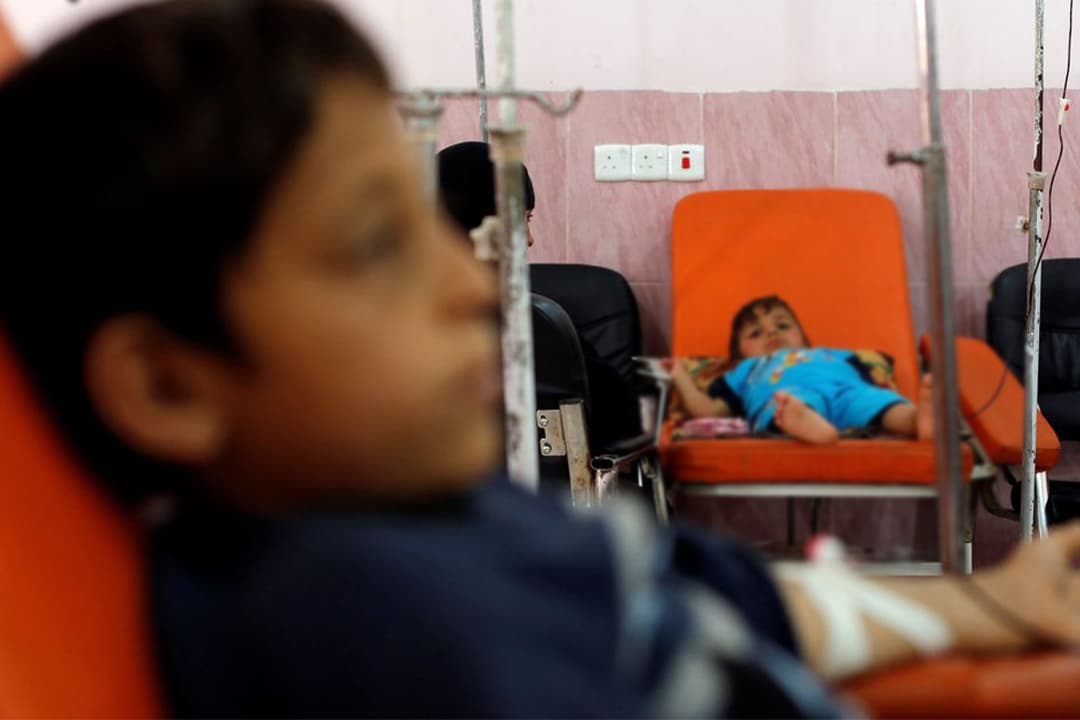
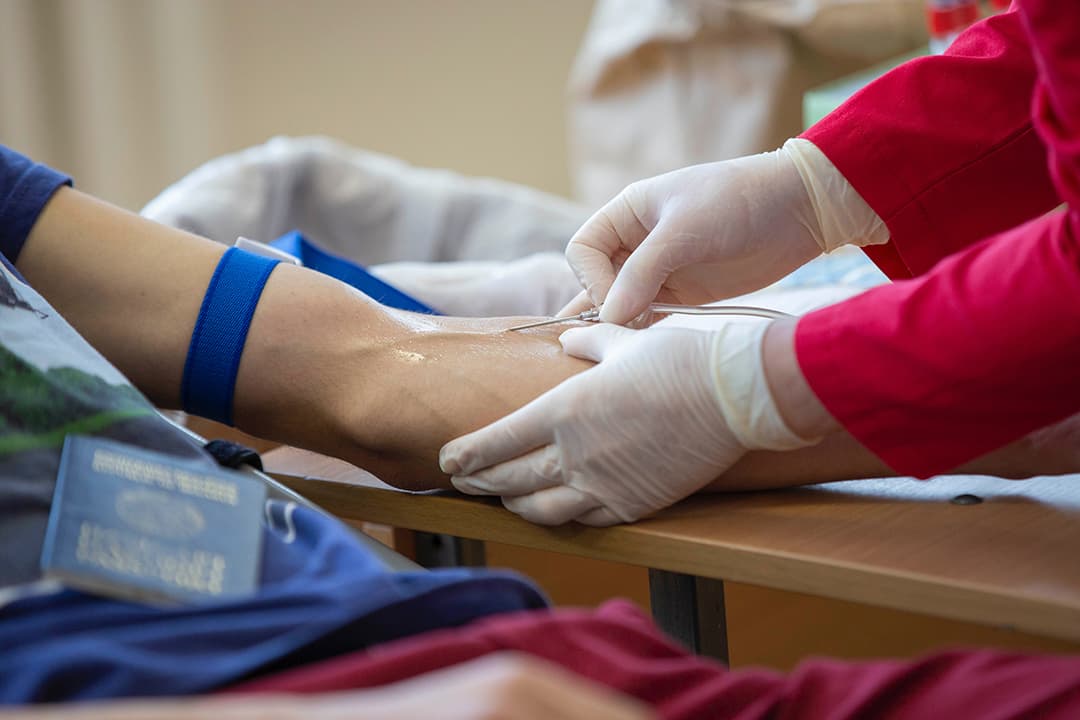
Thalassemia is a serious condition that can cause anemia, fatigue, and organ damage. It is a lifelong condition that requires regular medical treatment, including blood transfusions and chelation therapy. In severe cases, bone marrow transplantation may be necessary.
Thalassemia is prevalent in India, with an estimated 2.3 million people living with the condition. It is particularly common in certain states, including Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, and Gujarat. The high prevalence of thalassemia in India is due in part to the large population and the high frequency of consanguineous marriages (marriages between close relatives), which increases the risk of inherited genetic disorders.
The burden of thalassemia is particularly heavy on families affected by the condition. The medical costs of treating thalassemia can be overwhelming, and many families struggle to afford the necessary treatments. In addition, children with thalassemia may face discrimination and stigma, which can affect their education and opportunities in life.
One particularly heartbreaking aspect of thalassemia in India is the number of children who are born with the condition. Many families are unaware that they are carriers of the thalassemia gene and do not receive pre-natal testing. As a result, they may not be prepared for the challenges of caring for a child with thalassemia.
One such family is the Singh family, whose daughter Jyoti was diagnosed with thalassemia at just three months old. Jyoti's parents, who are both carriers of the thalassemia gene, had not received pre-natal testing and were shocked to learn of their daughter's condition. The family has struggled to afford Jyoti's medical treatment, which includes regular blood transfusions and chelation therapy. Despite these challenges, Jyoti's parents are determined to give her the best life possible and are grateful for the support they have received from the Thalassemia Society of India.
Another family affected by thalassemia is the Das family, whose son Rohit was diagnosed with the condition at just two months old. Rohit's parents, who are both carriers of the thalassemia gene, had not received pre-natal testing and were devastated to learn of their son's condition. Rohit requires regular blood transfusions and chelation therapy to survive, and the medical costs have put a tremendous strain on the family's finances. Rohit's parents have had to make difficult decisions, including leaving their jobs and selling their home, in order to afford his medical treatment.
Despite the challenges faced by families affected by thalassemia, there is hope for those living with the condition. Research is ongoing to develop new treatments and therapies for thalassemia, and there are a number of organizations and support groups available to provide assistance and support to those affected by the condition.
One such organization is the Thalassemia Society of India, which was founded in 1988 to support families affected by thalassemia and to raise awareness about the condition. The organization provides a range of services, including financial assistance for medical treatment, counseling, and support groups for families.